ESG - Environmental, Social & Governance
What is ESG?
Investors, customers, employees and other stakeholders are increasingly recognizing the critically important role companies and organizations play in managing environmental, social and governance risks and opportunities. In 2019, the Business Roundtable – chaired by JP Morgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon, and joined by 181 CEOs across all industrial sectors – released a statement describing the purpose of a corporation recognizing that corporate responsibility extends beyond just maximizing financial performance to shareholders.
ESG is a comprehensive, proactive approach that goes beyond a singular focus on financial performance for shareholders to recognize a company’s impact on society, the environment, and its own governance and is important for both shareholders and stakeholders alike.
Why is ESG important?
ESG is becoming a crucial component of business strategy and decision-making and offers an opportunity to enhance a company’s reputation and gain a competitive advantage. Here’s why ESG matters:
ESG is important for both shareholders and stakeholders alike. Here’s why ESG matters:
- Investor Demand: Investors are increasingly considering ESG factors in their investment decisions. Companies that focus on ESG tend to have more sustainable business models, which can lead to more consistent financial performance over time. Investors often view ESG commitment as a marker of reduced investment risk.
- Customer Demand: Consumers and stakeholders are increasingly concerned about the ethical, social, and environmental impact of the companies they support. Companies that prioritize ESG can enhance their reputation, attract loyal customers, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
- Attracting Talent & Engaging Employees: Today’s workforce increasingly values working for companies that align with their ethical and environmental values. A strong ESG commitment can help attract top talent and improve employee retention.
What is the difference between ESG and CSR?
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) are both frameworks that address a company’s impact on society and the environment. However, they differ in focus, scope, and how they are integrated into a company’s operations and strategy.
CSR typically refers to a company’s voluntary efforts to contribute to societal goals, such as philanthropy, ethical labor practices, and community engagement. CSR activities are often viewed as complementary but separate from the core business strategy. CSR initiatives are often less quantifiable and may not be rigorously measured or reported. While companies may report on their CSR activities, these reports are often more narrative in nature, focusing on the company’s contributions to social good rather than specific metrics. Accountability is more about meeting the expectations of stakeholders and maintaining a positive public image.
Conversely, ESG is a set of criteria used to evaluate a company’s overall sustainability and ethical impact and is generally integrated into a company’s core business strategy. ESG therefore influences how a company operates, manages risks, and identifies opportunities. ESG factors are quantifiable, and performance metrics are included in regulatory filings and are subject to scrutiny by investors and rating agencies. Investors and stakeholders use ESG criteria to assess the sustainability of a company’s operations, making it a critical factor in investment decisions.
While ESG and CSR can overlap, particularly in areas like environmental stewardship and ethical labor practices, ESG is typically more data-driven and integrated into business strategy, whereas CSR is often more about corporate philanthropy and public relations.
What are ESG factors?
ESG factors are criteria used to evaluate a company’s operations and its impact on the environment, society, and governance practices. These factors help investors, regulators, and stakeholders assess the sustainability, ethical considerations, and overall risk profile of a company. ESG factors are typically grouped into three main categories: Environmental, Social, and Governance.
Environmental (E): Focuses on how a company interacts with the natural environment and manages environmental risks.
Social (S): captures the company’s relationships with employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities in which it operates.
Governance (G): Pertains to the company’s decision-making processes, and accountability, leadership and organizational structures.
Why do companies need an ESG strategy?
Companies need a compelling ESG strategy for several reasons, driven by the evolving expectations of stakeholders, increased regulatory pressures, and the broader impact on business performance. Here are the key reasons why an ESG strategy is essential:
- Meet Stakeholder Expectations & Establish the Narrative
- Investor Demand: Investors are increasingly prioritizing companies that demonstrate strong ESG practices, as these are seen as indicators of long-term sustainability and proactive risk management. An ESG strategy makes a company more attractive to socially responsible investors and can lead to better access to capital.
- Proactive Messaging: leading the discussion of material ESG factors – internally and externally, enables leaders to communicate more effectively and circumvent third parties from drawing conclusions based on inaccurate information.
- Customer Preferences: Consumers are increasingly conscious of the ethical and environmental impact of their purchases and are demonstrating a willingness to spend accordingly. Companies with robust ESG strategies are more likely to attract and retain customers who prioritize sustainability and social responsibility.
- Employee Attraction and Retention: A strong ESG strategy can enhance a company’s reputation as an employer, attracting talent who want to work for organizations that align with their values. It also boosts employee engagement and retention by fostering a positive, more purposeful work environment.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Evolving Regulations: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly implementing laws and guidelines related to environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. An ESG strategy not only helps companies stay ahead of these regulations but offers the opportunity to proactively influence future regulation.
- Global Standards: International standards and frameworks like the Paris Agreement, the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and various environmental, social, and governance reporting standards are pushing companies to adopt and transparently report on ESG practices.
- Proactive Risk Management
- Environmental Risks: Climate change, resource scarcity, and environmental degradation pose significant risks to businesses. An ESG strategy helps companies mitigate these risks by adopting sustainable practices that reduce their environmental impact and associated risks.
- Social Risks: Issues like human rights abuses, labor disputes, and poor community relations can lead to reputational damage, legal liabilities, and operational disruptions. A proactive ESG strategy addresses these risks by ensuring ethical practices across the supply chain and in local communities.
- Governance Risks: Poor governance practices, such as lack of transparency, corruption, and weak oversight, can lead to financial mismanagement and scandals. A strong ESG strategy ensures robust governance structures that protect the company’s integrity and stakeholder interests.
- Long-term Value Creation
- Sustainable Growth: An ESG strategy lays the foundation for long-term business growth by aligning the company’s operations with sustainable practices that conserve resources, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact. This leads to cost savings and operational efficiencies in addition to protecting the plant.
- Brand Loyalty: Companies with strong ESG credentials often enjoy higher levels of customer loyalty and trust. This can translate into sustainable, long-term revenue growth as consumers increasingly prefer to buy from brands that align with their values.
- Enhanced Reputation and Trust
- Public Perception: A well-executed ESG strategy can enhance a company’s reputation among consumers, investors, and the broader public. This positive perception can lead to increased brand equity and market share.
- Crisis Resilience: Companies with strong ESG practices are often better equipped to handle crises, such as environmental disasters or social controversies. Their commitment to transparency, ethical practices, and stakeholder engagement can help them navigate challenges more effectively and maintain trust.
- Future-proofing the Business
- Adaptation to Megatrends: Global megatrends, such as climate change, resource depletion, and demographic shifts, are reshaping the business landscape. An ESG strategy helps companies adapt to these changes, ensuring their business models remain viable in the long term.
- Resilience to Disruptions: Companies with robust ESG practices are often more resilient to disruptions, such as supply chain interruptions, regulatory changes, or shifts in consumer behavior. This resilience can be a key differentiator in a rapidly changing world.
Summary
An ESG strategy is essential for companies to meet the growing expectations of stakeholders, comply with regulatory requirements, manage risks, create long-term value, enhance their reputation, and future-proof their operations. By integrating ESG considerations into their business strategies, companies can achieve sustainable growth, build trust with stakeholders, and position themselves for success in an increasingly sustainability-focused world.
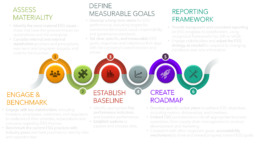
Steps to Develop an ESG Strategy
To take advantage of the many benefits of ESG while doing their part to realize a more equitable society and sustainable environment, businesses should develop formal ESG programs. High-level steps have been provided below:
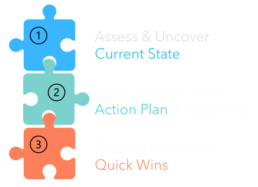
How We Engage - It's as Easy as 1,2,3
Envision RISE can support your initiatives at any stage with flexible service options, including Hourly Staff Augmentation, Time & Materials, or Firm Fixed Price. It is easy to get started.
Got Questions? Please email us at info@envisionRISE.com